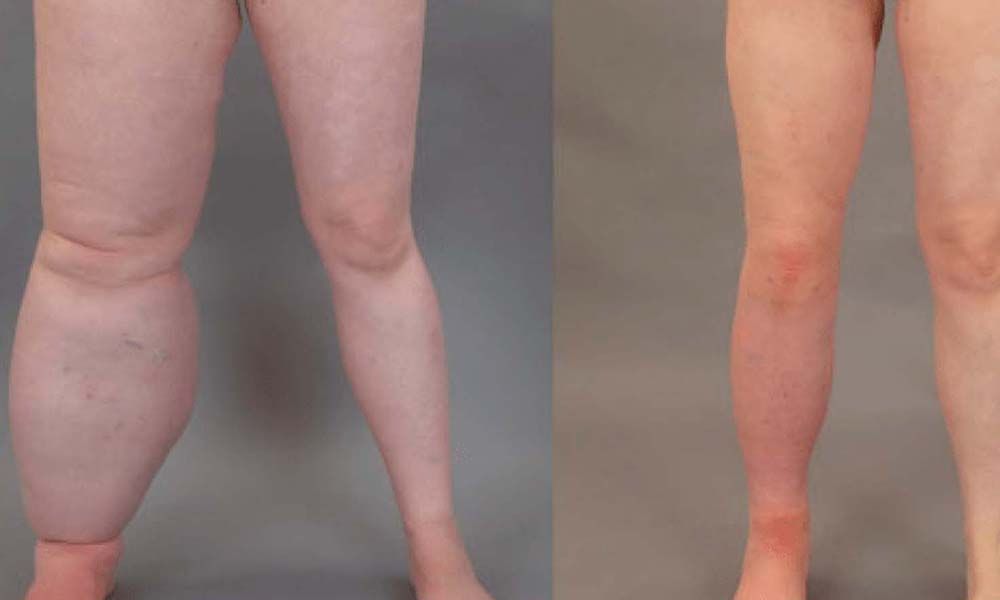
Lymphedema refers to the swelling of the upper or lower limb due to the accumulation of lymph fluids under the skin causing disfigurement, discomfort and affecting daily activities. This occurs following disruption of the drainage of the lymph fluids from the skin through the lymphatic channels to lymph nodes and ultimately into the circulation draining into the major venous system.
The cause for lymphedema can be primary due to abnormalities in the lymphatic system drainage as part of development abnormalities since birth/ hereditary. Although the presence of such lymphedema is variable in age groups, lymphedema congenital (<2 years), lymphedema praecox (2-35 years) and lymphedema tarda (>35 years). The person first notices the abnormal swelling is generally following trivial trauma, insect bite or skin infections. However, the major cause of lymphedema throughout the world is secondary lymphedema. Secondary lymphedema occurs following disruption of lymphatic system drainage subsequent to parasitic infection like filariasis (spread by mosquitoes), lymph node surgeries as treatment of breast cancers/gynecological cancers, radiation therapy, trauma.
Most common cause of lymphedema is filariasis but there is increase in disease burden due to increase in prevalence of breast cancers and gynaecological cancers.
Although lymphedema commonly affects upper and lower limbs, it can affect genitalia, head and neck areas as well. It can present as mild swelling, gross disfigurement like elephantiasis (elephant limb), thick irregular skin and non-healing ulcers.
The diagnosis of lymphedema is mainly based on its clinical findings. However, there are radiological imaging modalities to assess the lymphatic vessels and drainage pattern ( lymphoscintigraphy / MR lymphography) and advanced technology that can help in visualizing the drainage of lymph through lymphatic channels in real-time using infra-red cameras.
Lymphedema is an incurable condition but it can be well controlled by different treatment modalities.
Complex decongestive therapy involves two phases,
- Intensive phase
- Maintenance phase.
In the intensive phase, done under the supervision of trained lymphedema therapist/ doctors has four components including skin hygiene care, decongestive exercises, manual lymphatic drainage, and multi-layered lymphatic drainage.
After this phase, there will be a reduction in the size of the involved area to about 40-60%. Then therapy is switched to the maintenance phase, done by the patient at home by taking care of himself / herself including skin hygiene care, exercises and using the pressure garment.
Surgical treatment for lymphedema includes liposuction and skin debulking/ excision surgeries. Recent advances in the field of microsurgery had rediscovered the options to treat lymphedema physiologically by improving the lymph drainage using microvascular surgeries like vascularised lymph node transfer, vascularised lymphatic tissue transfer, and lymphatico-venous anastomosis.
People suffering from lymphedema can improve there lifestyle by the above-mentioned treatment to improve the quality of skin appearance, reduce disfigurement and discomfort; also these treatment slows or stops the disease progression.